Server tools
Connect your assistant to external data & systems.
Tools enable your assistant to connect to external data and systems. You can define a set of tools that the assistant has access to, and the assistant will use them where appropriate based on the conversation.
Overview
Many applications require assistants to call external APIs to get real-time information. Tools give your assistant the ability to make external function calls to third party apps so you can get real-time information.
Here are a few examples where tools can be useful:
- Fetching data: enable an assistant to retrieve real-time data from any REST-enabled database or 3rd party integration before responding to the user.
- Taking action: allow an assistant to trigger authenticated actions based on the conversation, like scheduling meetings or initiating order returns.
To interact with Application UIs or trigger client-side events use client tools instead.
Tool configuration
ElevenLabs agents can be equipped with tools to interact with external APIs. Unlike traditional requests, the assistant generates query, body, and path parameters dynamically based on the conversation and parameter descriptions you provide.
All tool configurations and parameter descriptions help the assistant determine when and how to use these tools. To orchestrate tool usage effectively, update the assistant’s system prompt to specify the sequence and logic for making these calls. This includes:
- Which tool to use and under what conditions.
- What parameters the tool needs to function properly.
- How to handle the responses.
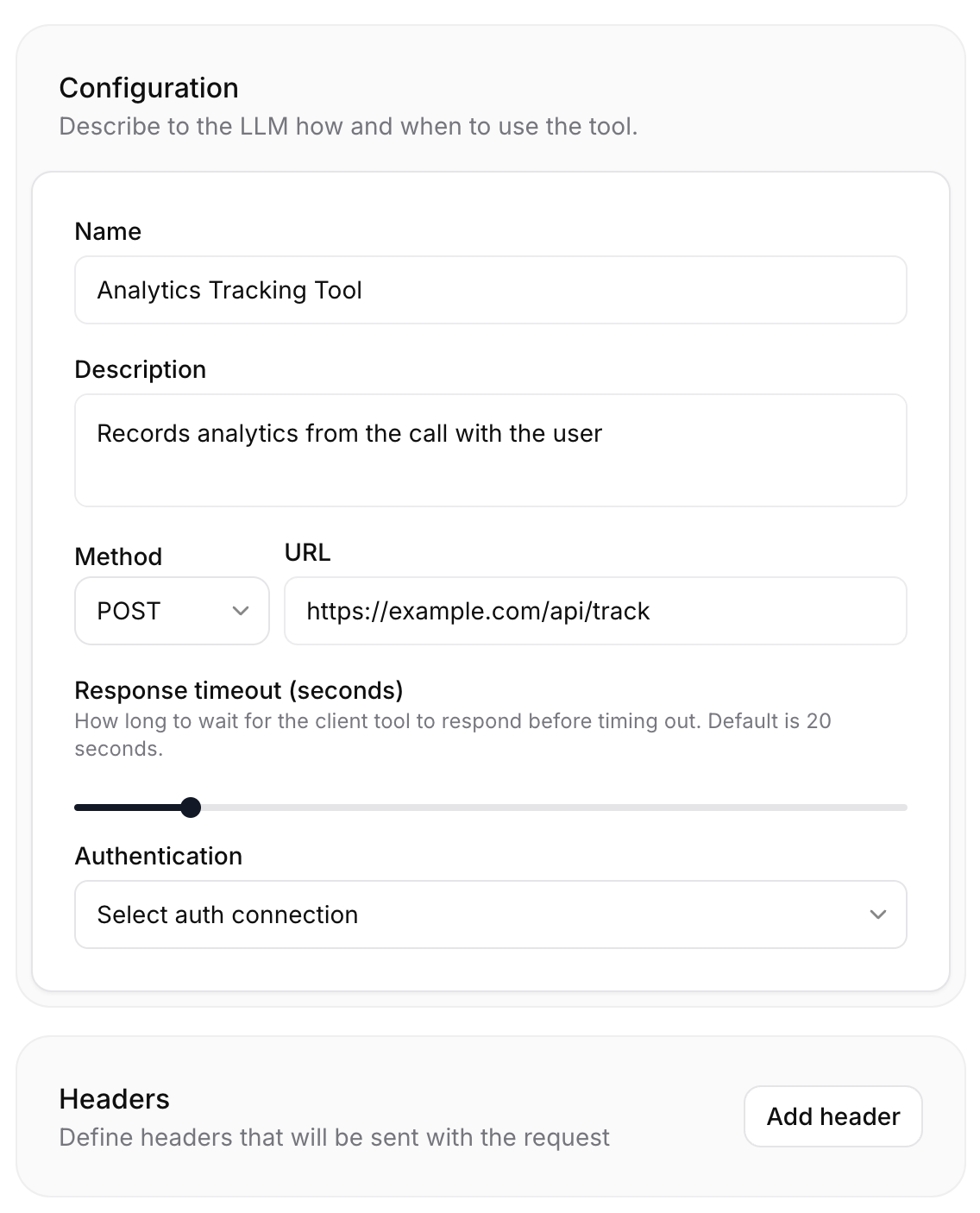
Configuration
Authentication
Headers
Path parameters
Body parameters
Query parameters
Dynamic variable assignment
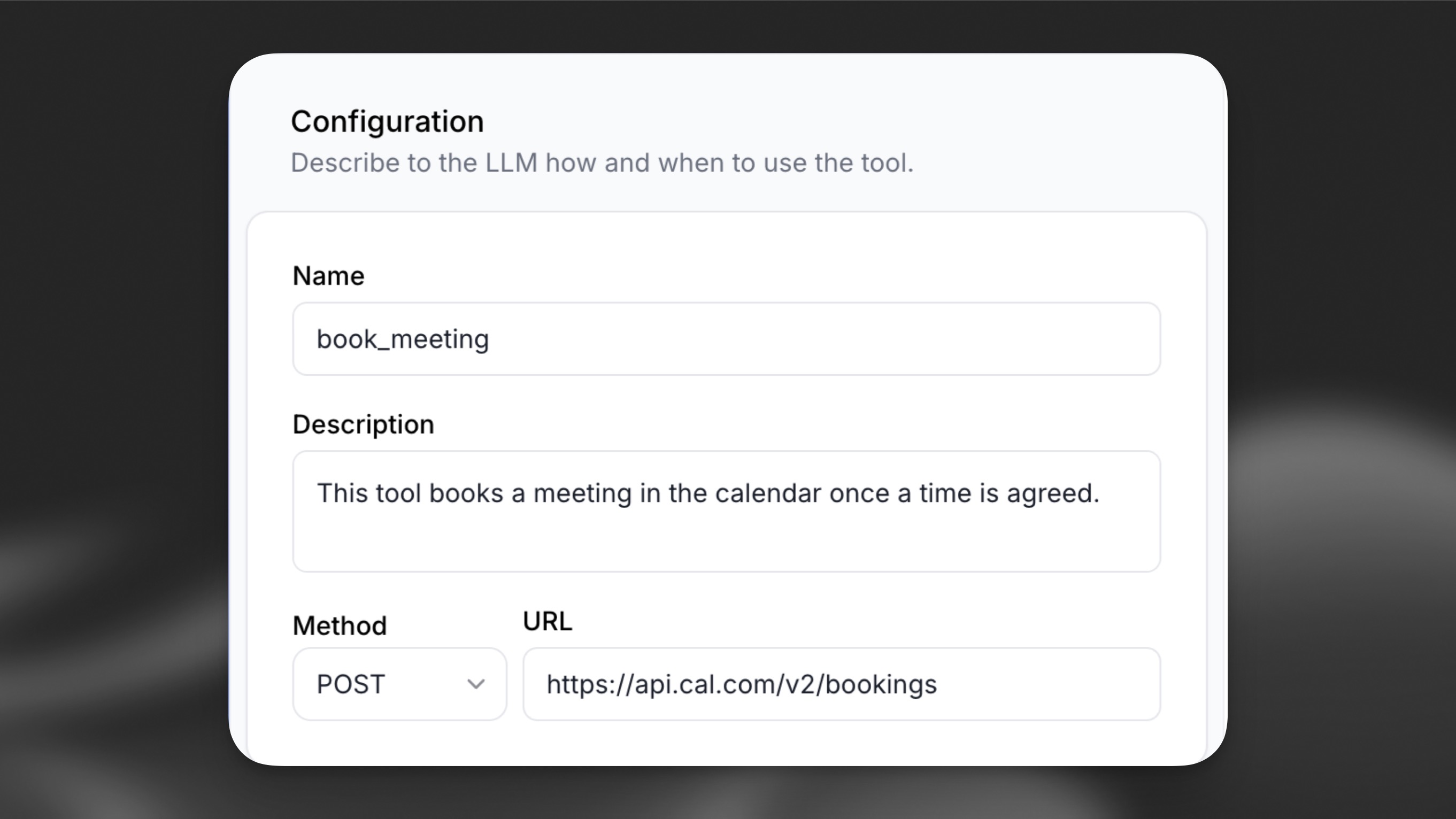
Define a high-level Name and Description to describe the tool’s purpose. This helps the LLM understand the tool and know when to call it.
If the API requires path parameters, include variables in the URL path by wrapping them in curly
braces {}, for example: /api/resource/{id} where id is a path parameter.
Guide
In this guide, we’ll create a weather assistant that can provide real-time weather information for any location. The assistant will use its geographic knowledge to convert location names into coordinates and fetch accurate weather data.
Configure the weather tool
First, on the Agent section of your agent settings page, choose Add Tool. Select Webhook as the Tool Type, then configure the weather API integration:
Weather Tool Configuration
Configuration
Path Parameters
An API key is not required for this tool. If one is required, this should be passed in the headers and stored as a secret.
Orchestration
Configure your assistant to handle weather queries intelligently with this system prompt:
Test your assistant by asking about the weather in different locations. The assistant should handle specific locations (“What’s the weather in Tokyo?”) and ask for clarification after general queries (“How’s the weather looking today?”).
Supported Authentication Methods
ElevenLabs Agents supports multiple authentication methods to securely connect your tools with external APIs. Authentication methods are configured in your agent settings and then connected to individual tools as needed.
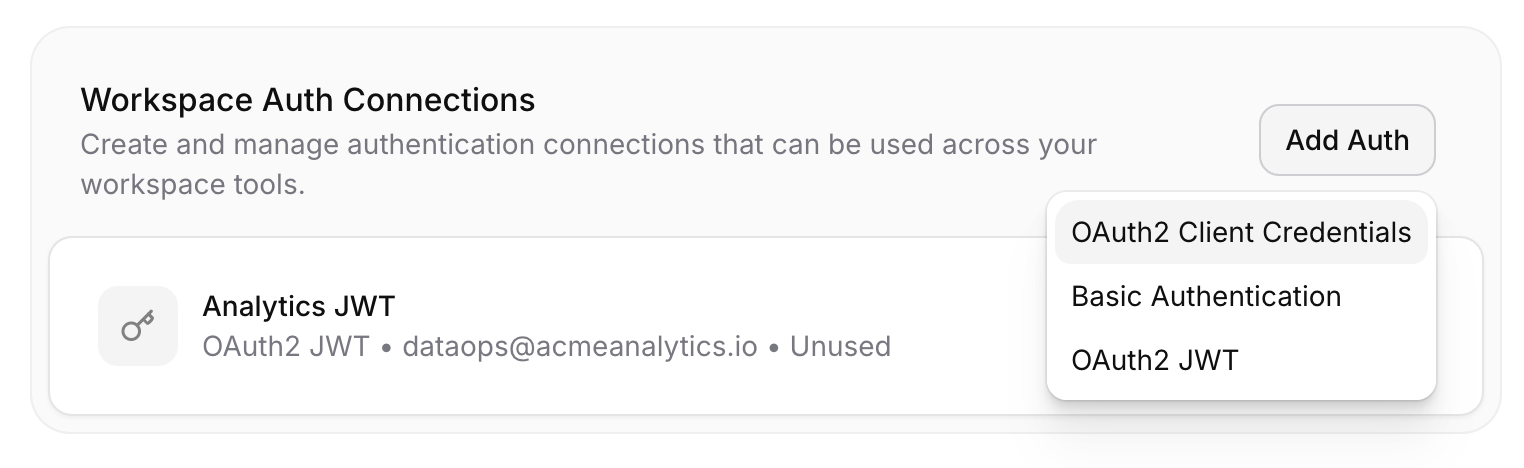
Once configured, you can connect these authentication methods to your tools and manage custom headers in the tool configuration:
OAuth2 Client Credentials
Automatically handles the OAuth2 client credentials flow. Configure with your client ID, client secret, and token URL (e.g., https://api.example.com/oauth/token). Optionally specify scopes as comma-separated values and additional JSON parameters. Set up by clicking Add Auth on Workspace Auth Connections on the Agent section of your agent settings page.
OAuth2 JWT
Uses JSON Web Token authentication for OAuth 2.0 JWT Bearer flow. Requires your JWT signing secret, token URL, and algorithm (default: HS256). Configure JWT claims including issuer, audience, and subject. Optionally set key ID, expiration (default: 3600 seconds), scopes, and extra parameters. Set up by clicking Add Auth on Workspace Auth Connections on the Agent section of your agent settings page.
Basic Authentication
Simple username and password authentication for APIs that support HTTP Basic Auth. Set up by clicking Add Auth on Workspace Auth Connections in the Agent section of your agent settings page.
Bearer Tokens
Token-based authentication that adds your bearer token value to the request header. Configure by adding a header to the tool configuration, selecting Secret as the header type, and clicking Create New Secret.
Custom Headers
Add custom authentication headers with any name and value for proprietary authentication methods. Configure by adding a header to the tool configuration and specifying its name and value.
Best practices
Name tools intuitively, with detailed descriptions
If you find the assistant does not make calls to the correct tools, you may need to update your tool names and descriptions so the assistant more clearly understands when it should select each tool. Avoid using abbreviations or acronyms to shorten tool and argument names.
You can also include detailed descriptions for when a tool should be called. For complex tools, you should include descriptions for each of the arguments to help the assistant know what it needs to ask the user to collect that argument.
Name tool parameters intuitively, with detailed descriptions
Use clear and descriptive names for tool parameters. If applicable, specify the expected format for a parameter in the description (e.g., YYYY-mm-dd or dd/mm/yy for a date).
Consider providing additional information about how and when to call tools in your assistant’s system prompt
Providing clear instructions in your system prompt can significantly improve the assistant’s tool calling accuracy. For example, guide the assistant with instructions like the following:
Provide context for complex scenarios. For example:
LLM selection
When using tools, we recommend picking high intelligence models like GPT-4o mini or Claude 3.5 Sonnet and avoiding Gemini 1.5 Flash.
It’s important to note that the choice of LLM matters to the success of function calls. Some LLMs can struggle with extracting the relevant parameters from the conversation.
Tool Call Sounds
You can configure ambient audio to play during tool execution to enhance the user experience. Learn more about Tool Call Sounds.