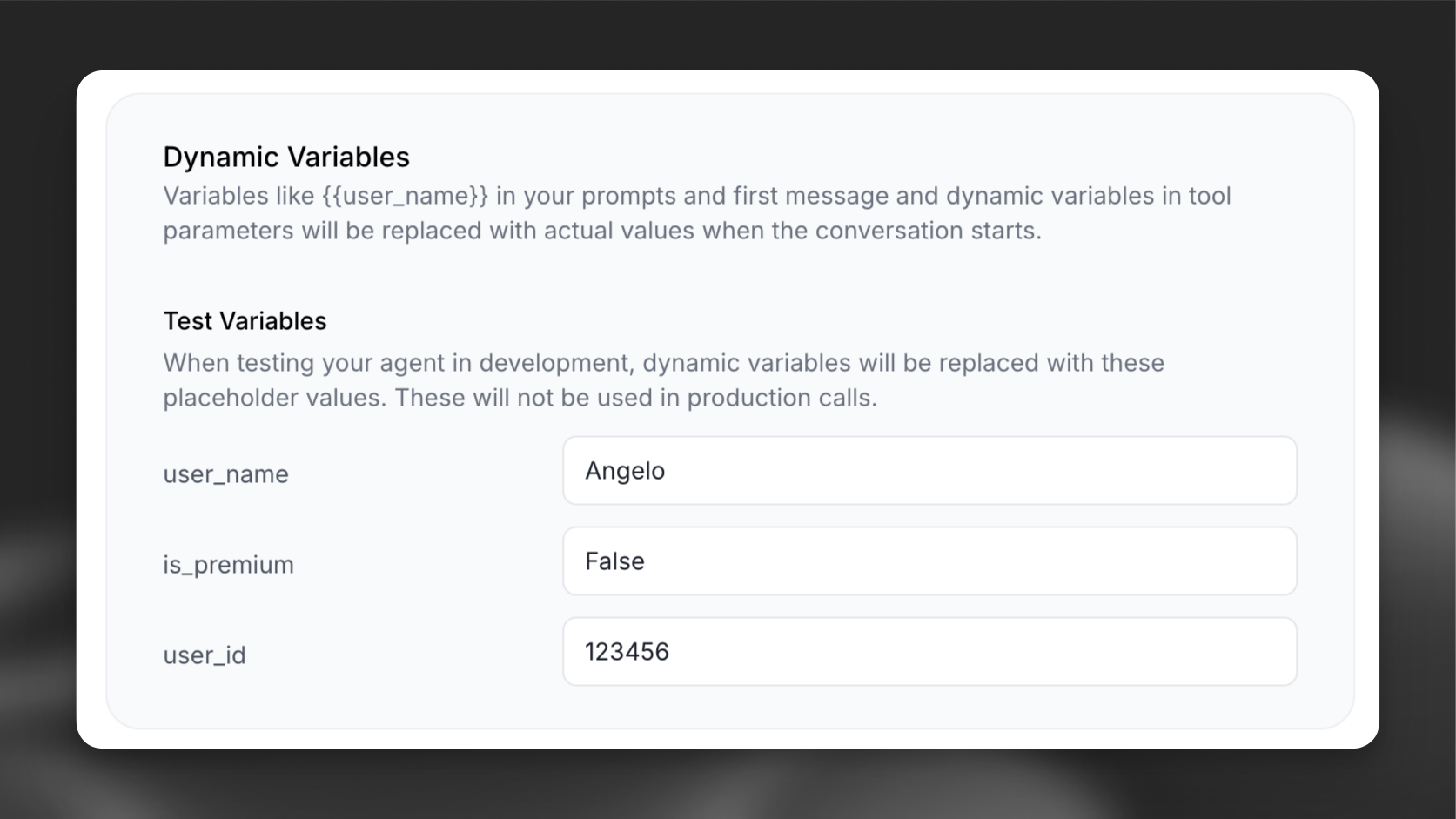
Dynamic variables
Dynamic variables allow you to inject runtime values into your agent’s messages, system prompts, and tools. This enables you to personalize each conversation with user-specific data without creating multiple agents.
Overview
Dynamic variables can be integrated into multiple aspects of your agent:
- System prompts to customize behavior and context
- First messages to personalize greetings
- Tool parameters and headers to pass user-specific data
Here are a few examples where dynamic variables are useful:
- Personalizing greetings with user names
- Including account details in responses
- Passing data to tool calls
- Customizing behavior based on subscription tiers
- Accessing system information like conversation ID or call duration
Dynamic variables are ideal for injecting user-specific data that shouldn’t be hardcoded into your agent’s configuration.
System dynamic variables
Your agent has access to these automatically available system variables:
system__agent_id- Unique identifier of the agent that initiated the conversation (stays stable throughout the conversation)system__current_agent_id- Unique identifier of the currently active agent (changes after agent transfers)system__caller_id- Caller’s phone number (voice calls only)system__called_number- Destination phone number (voice calls only)system__call_duration_secs- Call duration in secondssystem__time_utc- Current UTC time (ISO format)system__time- Current time in the specified timezone (human-readable format, e.g., “Friday, 12:33 12 December 2025”)system__timezone- User-provided timezone (must be valid for tzinfo)system__conversation_id- ElevenLabs’ unique conversation identifiersystem__call_sid- Call SID (twilio calls only)
System variables:
- Are available without runtime configuration
- Are prefixed with
system__(reserved prefix) - In system prompts: Set once at conversation start (value remains static)
- In tool calls: Updated at execution time (value reflects current state)
system__ prefix.Secret dynamic variables
Secret dynamic variables are populated in the same way as normal dynamic variables but indicate to our ElevenAgents that these should only be used in dynamic variable headers and never sent to an LLM provider as part of an agent’s system prompt or first message.
We recommend using these for auth tokens or private IDs that should not be sent to an LLM. To create a secret dynamic variable, simply prefix the dynamic variable with secret__.
Updating dynamic variables from tools
Tool calls can create or update dynamic variables if they return a valid JSON object. To specify what should be extracted, set the object path(s) using dot notation. If the field or path doesn’t exist, nothing is updated.
Example of a response object and dot notation:
- Status corresponds to the path:
response.status - The first user’s email in the users array corresponds to the path:
response.users.0.email
To update a dynamic variable to be the first user’s email, set the assignment like so.
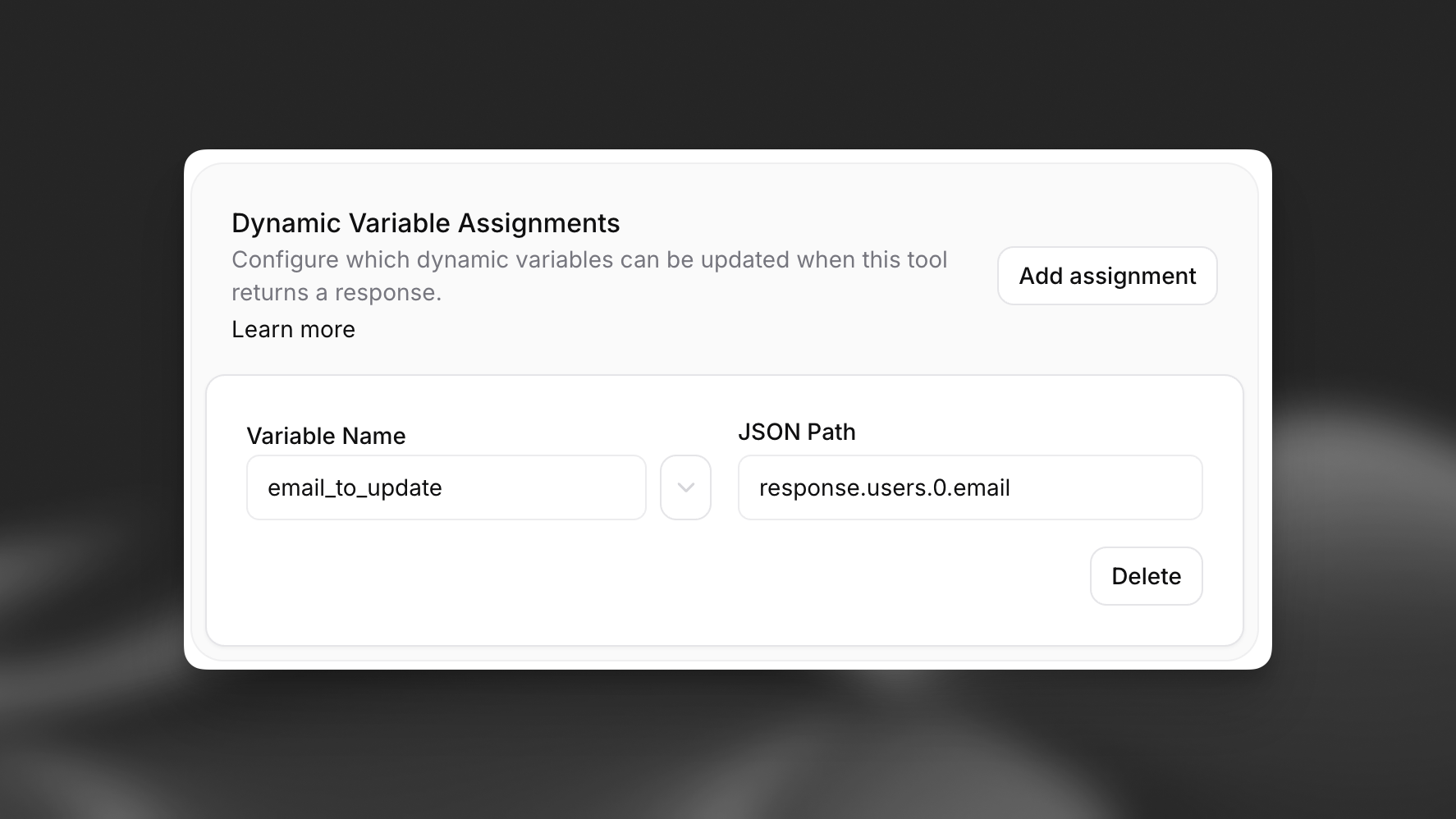
Assignments are a field of each server tool, that can be found documented here.
Guide
Prerequisites
- An ElevenLabs account
- A configured ElevenLabs Conversational Agent (create one here)
Define dynamic variables in prompts
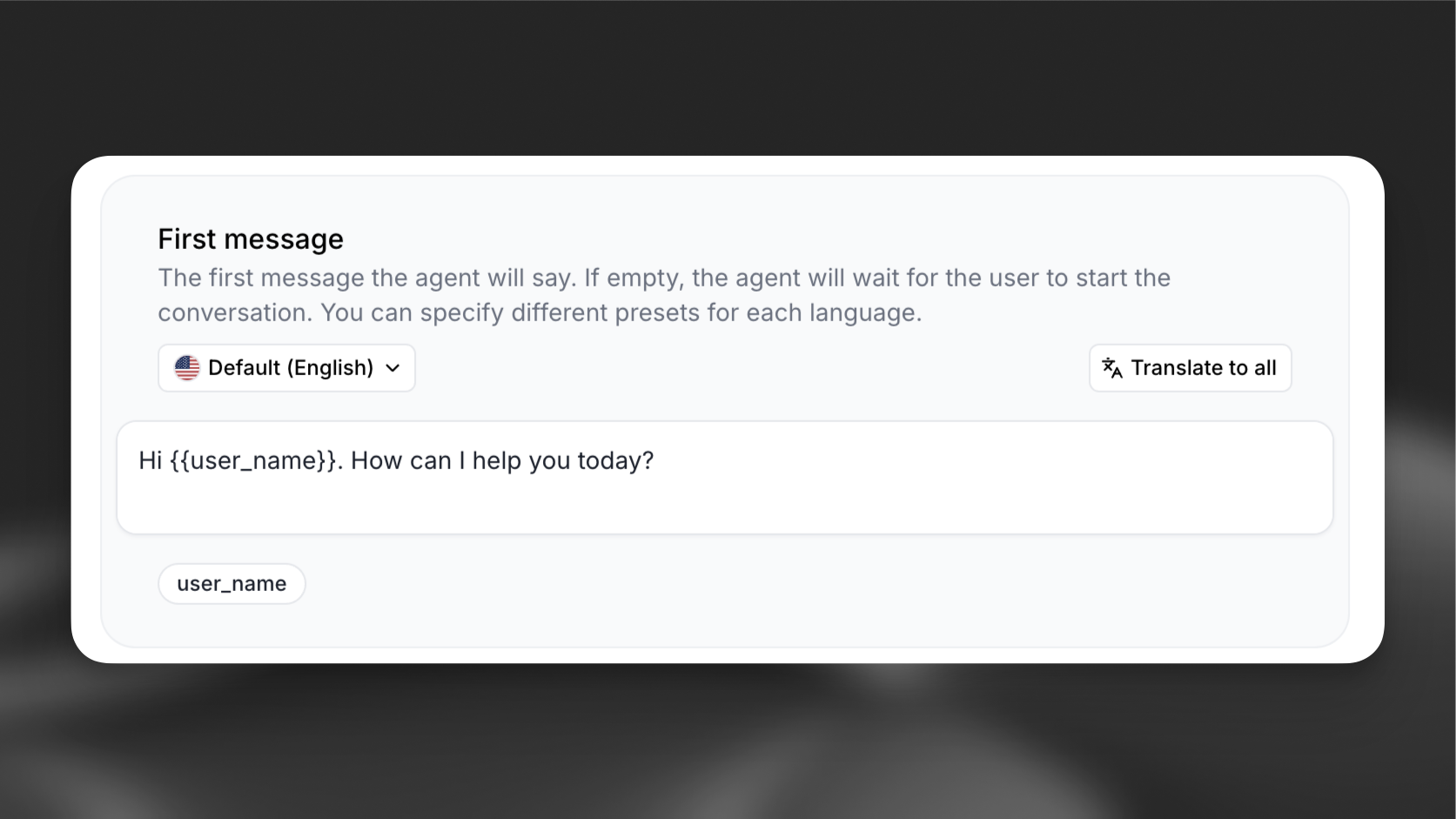
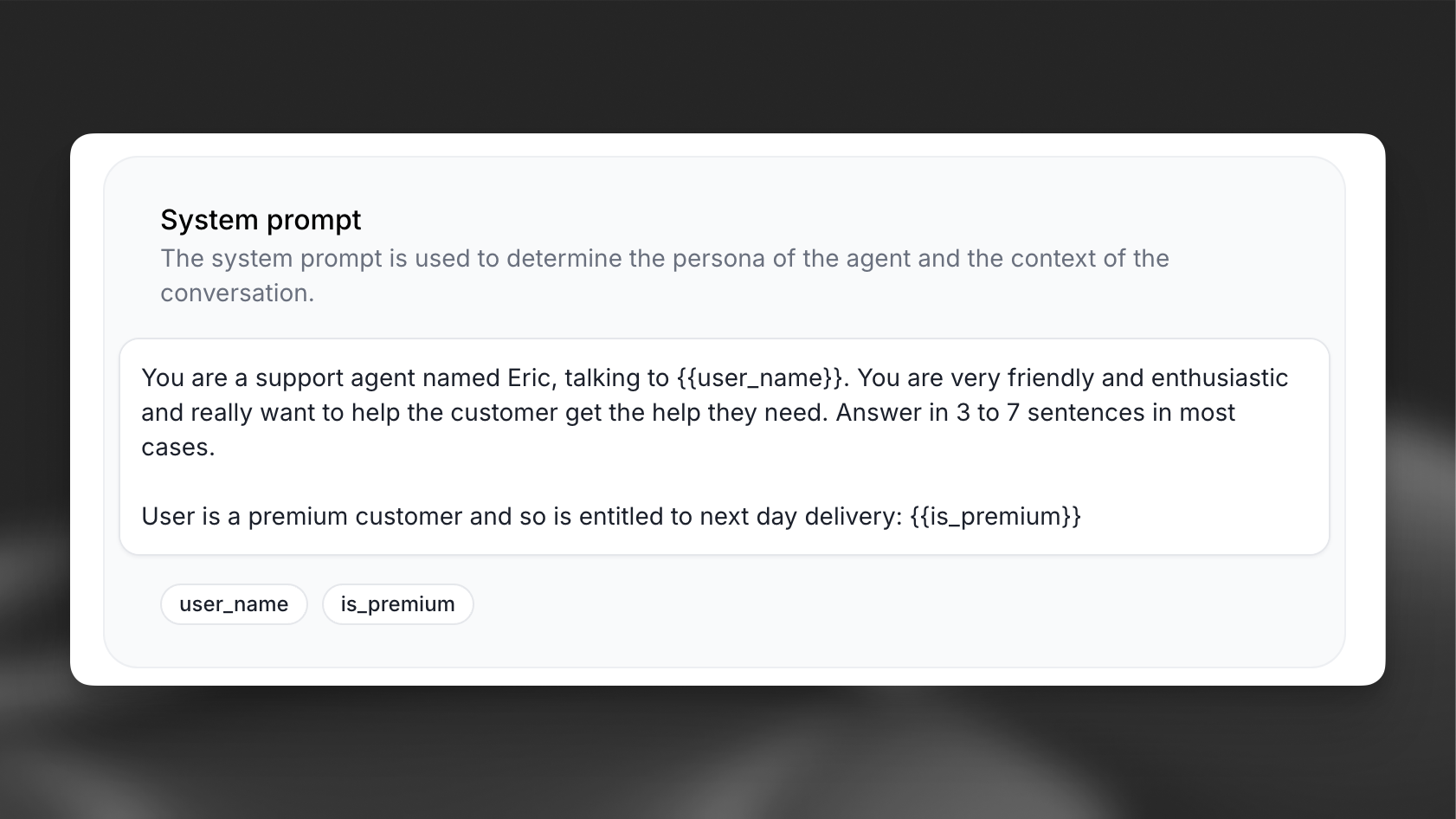
Add variables using double curly braces {{variable_name}} in your:
- System prompts
- First messages
- Tool parameters
Define dynamic variables in tools
You can also define dynamic variables in the tool configuration.
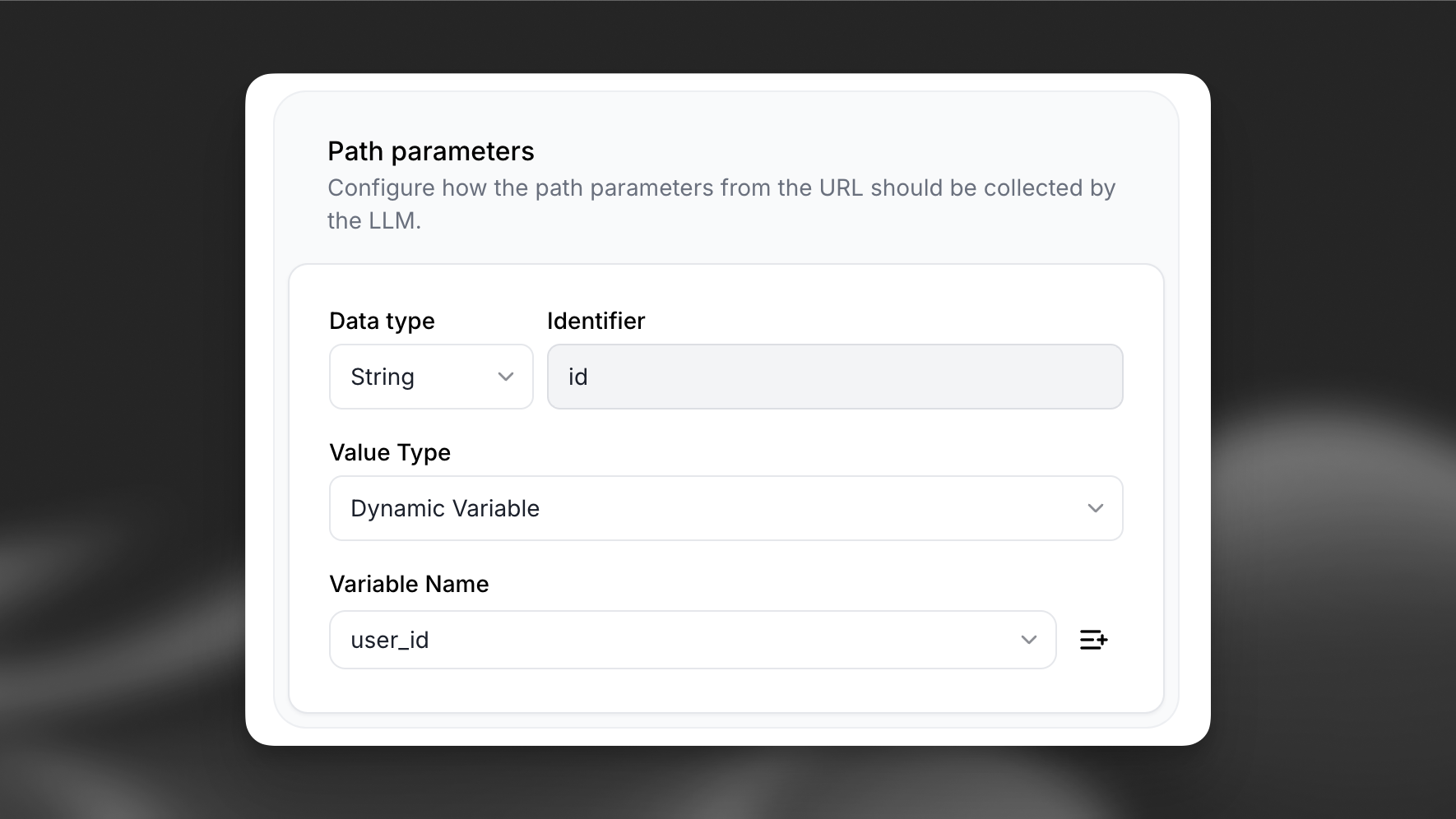
To create a new dynamic variable, set the value type to Dynamic variable and click the + button.
Pass variables at runtime
When starting a conversation, provide the dynamic variables in your code:
Ensure you have the latest SDK installed.
Public Talk-to Page Integration
The public talk-to page supports dynamic variables through URL parameters, enabling you to personalize conversations when sharing agent links. This is particularly useful for embedding personalized agents in websites, emails, or marketing campaigns.
URL Parameter Methods
There are two methods to pass dynamic variables to the public talk-to page:
Method 1: Base64-Encoded JSON
Pass variables as a base64-encoded JSON object using the vars parameter:
The vars parameter contains base64-encoded JSON:
Method 2: Individual Query Parameters
Pass variables using var_ prefixed query parameters:
Parameter Precedence
When both methods are used simultaneously, individual var_ parameters take precedence over the base64-encoded variables to prevent conflicts:
In this example, user_name will be “John” (from var_user_name) instead of “Jane” (from the base64-encoded vars).
Implementation Examples
JavaScript URL Generation
Python URL Generation
Manual URL Construction
Supported Types
Dynamic variables support these value types:
Troubleshooting
Variables not replacing
Verify that:
- Variable names match exactly (case-sensitive)
- Variables use double curly braces:
{{ variable_name }} - Variables are included in your dynamic_variables object
Type errors
Ensure that:
- Variable values match the expected type
- Values are strings, numbers, or booleans only