MCP integration security
Tips for securely integrating third-party Model Context Protocol servers with your ElevenLabs conversational agents.
User Responsibility
You are responsible for the security, compliance, and behavior of any third-party MCP server you integrate with your ElevenLabs conversational agents. ElevenLabs provides the platform for integration but does not manage, endorse, or secure external MCP servers.
Overview
Integrating external servers via the Model Context Protocol (MCP) can greatly enhance your ElevenLabs conversational agents. However, this also means connecting to systems outside of ElevenLabs’ direct control, which introduces important security considerations. As a user, you are responsible for the security and trustworthiness of any third-party MCP server you choose to integrate.
This guide outlines key security practices to consider when using MCP server integrations within ElevenLabs.
Tool approval controls
ElevenLabs provides built-in security controls through tool approval modes that help you manage the security risks associated with MCP tool usage. These controls allow you to balance functionality with security based on your specific needs.
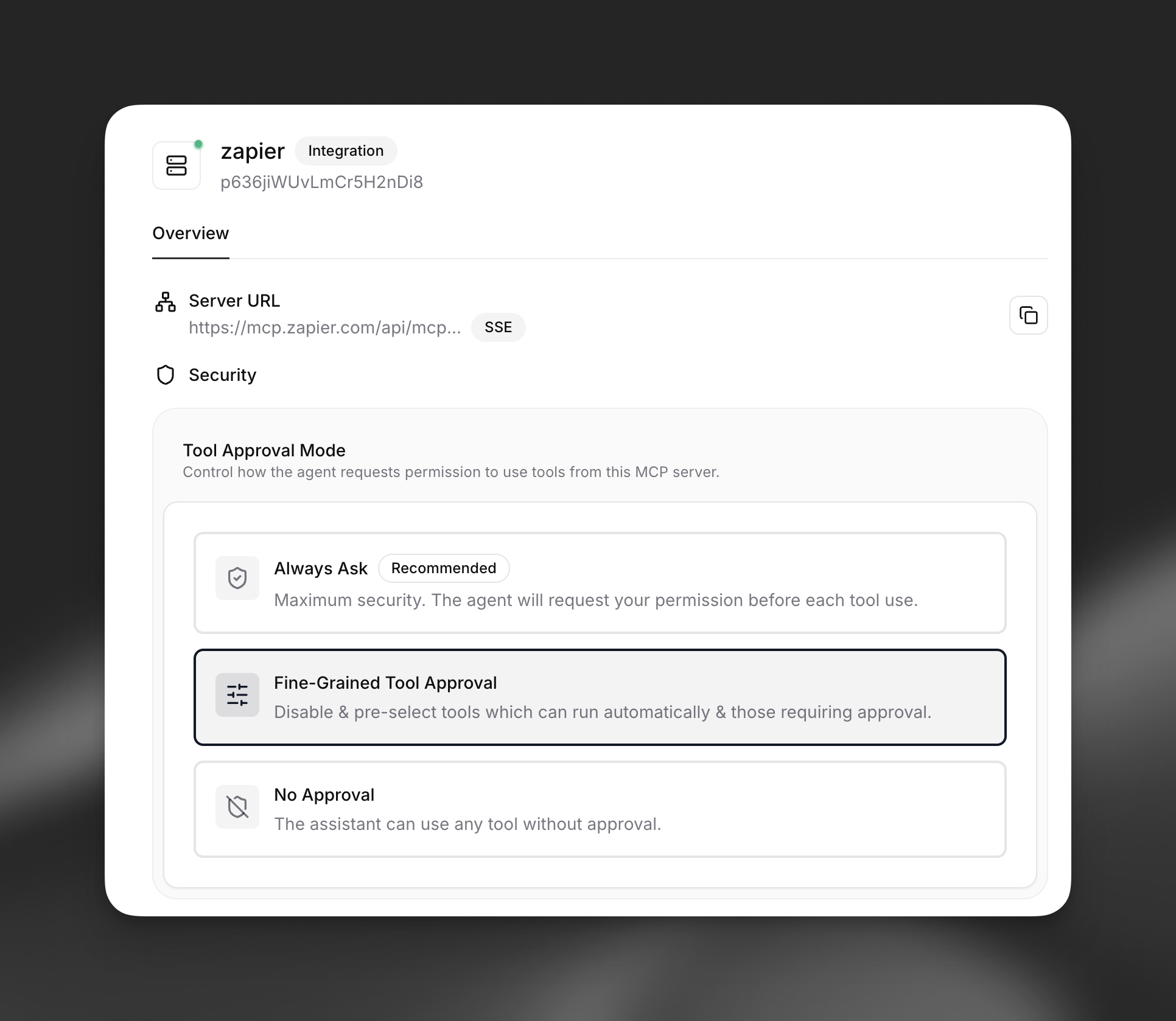
Approval mode options
- Always Ask (Recommended): Provides maximum security by requiring explicit approval for every tool execution. This mode ensures you maintain full control over all MCP tool usage.
- Fine-Grained Tool Approval: Allows you to configure approval requirements on a per-tool basis, enabling automatic execution of trusted tools while requiring approval for sensitive operations.
- No Approval: Permits unrestricted tool usage without approval prompts. Only use this mode with thoroughly vetted and highly trusted MCP servers.
Fine-grained security controls
Fine-Grained Tool Approval mode provides the most flexible security configuration, allowing you to classify each tool based on its risk profile:
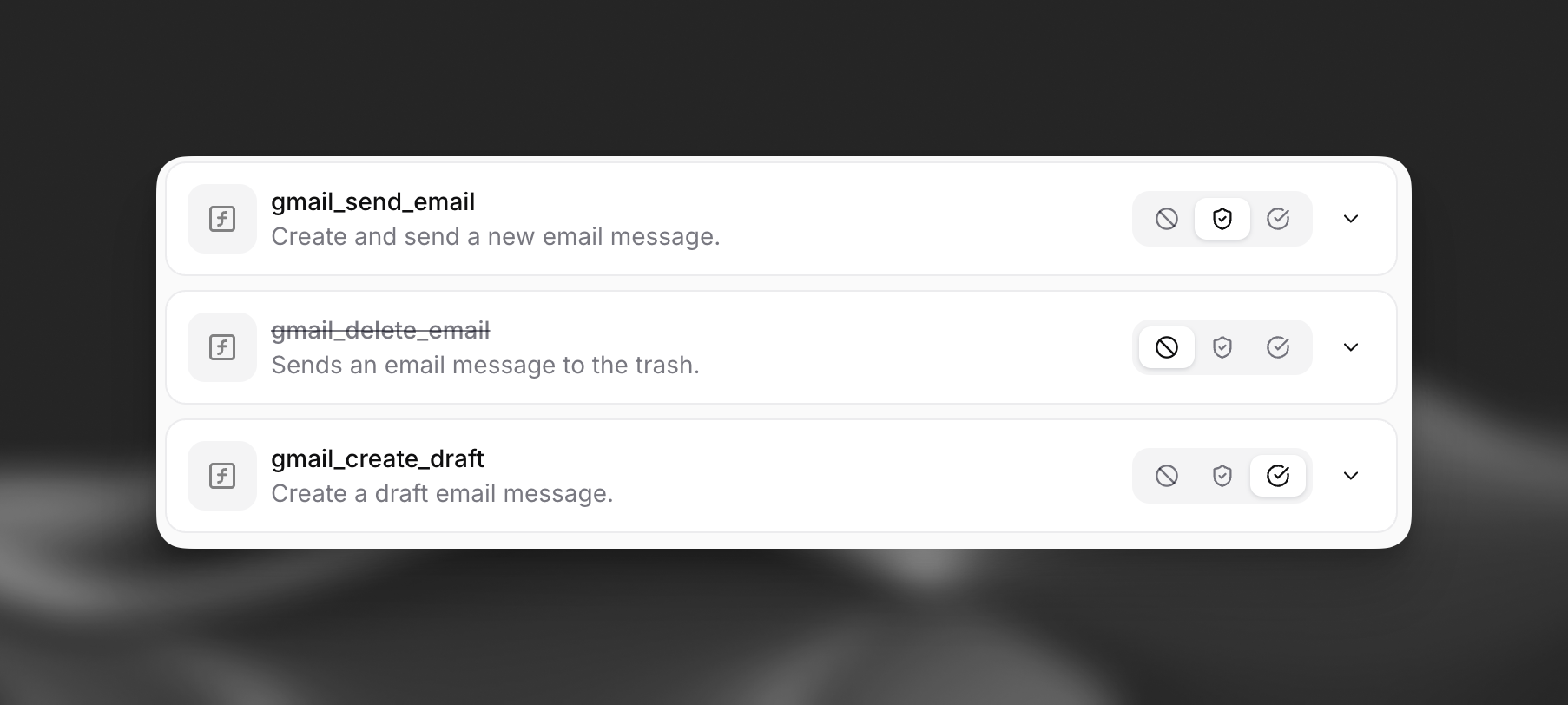
- Auto-approved tools: Suitable for low-risk, read-only operations or tools you completely trust
- Approval-required tools: For tools that modify data, access sensitive information, or perform potentially risky operations
- Disabled tools: Completely block tools that are unnecessary or pose security risks
Even with approval controls in place, carefully evaluate the trustworthiness of MCP servers and understand what each tool can access or modify before integration.
Security tips
1. Vet your MCP servers
- Trusted Sources: Only integrate MCP servers from sources you trust and have verified. Understand who operates the server and their security posture.
- Understand Capabilities: Before integrating, thoroughly review the tools and data resources the MCP server exposes. Be aware of what actions its tools can perform (e.g., accessing files, calling external APIs, modifying data). The MCP
destructiveHintandreadOnlyHintannotations can provide clues but should not be solely relied upon for security decisions. - Review Server Security: If possible, review the security practices of the MCP server provider. For MCP servers you develop, ensure you follow general server security best practices and the MCP-specific security guidelines.
2. Data sharing and privacy
- Data Flow: Be aware that when your agent uses an integrated MCP server, data from the conversation (which may include user inputs) will be sent to that external server.
- Sensitive Information: Exercise caution when allowing agents to send Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or other sensitive data to an MCP server. Ensure the server handles such data securely and in compliance with relevant privacy regulations.
- Purpose Limitation: Configure your agents and prompts to only share the necessary information with MCP server tools to perform their tasks.
3. Credential and connection security
- Secure Storage: If an MCP server requires API keys or other secrets for authentication, use any available secret management features within the ElevenLabs platform to store these credentials securely. Avoid hardcoding secrets.
- HTTPS: Ensure connections to MCP servers are made over HTTPS to encrypt data in transit.
- Network Access: If the MCP server is on a private network, ensure appropriate firewall rules and network ACLs are in place.
4. Understand code execution risks
- Remote Execution: Tools exposed by an MCP server execute code on that server. While this is the basis of their functionality, it’s a critical security consideration. Malicious or poorly secured tools could pose a risk.
- Input Validation: Although the MCP server is responsible for validating inputs to its tools, be mindful of the data your agent might send. The LLM should be guided to use tools as intended.
5. Add guardrails
- Prompt Injections: Connecting to untrusted external MCP servers exposes the risk of prompt injection attacks. Ensure to add thorough guardrails to your system prompt to reduce the risk of exposure to a malicious attack.
- Tool Approval Configuration: Use the appropriate approval mode for your security requirements. Start with “Always Ask” for new integrations and only move to less restrictive modes after thorough testing and trust establishment.
6. Monitor and review
- Logging (Server-Side): If you control the MCP server, implement comprehensive logging of tool invocations and data access.
- Regular Review: Periodically review your integrated MCP servers. Check if their security posture has changed or if new tools have been added that require re-assessment.
- Approval Patterns: Monitor tool approval requests to identify unusual patterns that might indicate security issues or misuse.
Disclaimer
Important Disclaimer
By enabling MCP server integrations, you acknowledge that this may involve data sharing with third-party services not controlled by ElevenLabs. This could incur additional security risks. Please ensure you fully understand the implications, vet the security of any MCP server you integrate, and adhere to these security guidelines before proceeding.
For general information on the Model Context Protocol, refer to official MCP documentation and community resources.