Text to Speech vs Speech to Text: jaka jest różnica?
Poznaj różnice między technologią text to speech a speech to text.
Wyobraź sobie: jedziesz do pracy, a twój smartfon czyta ci nieprzeczytane maile dziękizamiana tekstu na mowę (TTS). Co lepsze, możesz odpowiedzieć bez dotykania telefonu i odrywania wzroku od drogi – wszystko dziękizamiana mowy na tekst (STT).
Te technologie to nie tylko ciekawostka z przyszłości. Szybko stają się częścią codzienności, ułatwiając życie i zwiększając dostępność.
Przyjrzyjmy się bliżej TTS i STT opartym na AI – czym są, czym się różnią, jak działają, na co zwrócić uwagę przy wyborze dostawcy i jak są wykorzystywane w różnych branżach.
Różnice między TTS a tekstem z mowy
Jest kilka kluczowych różnic międzyTTS a technologią tekst-z-mowy. Oto one.
Funkcje
TTS zamienia tekst na mowę, a Speech to Text (STT) robi odwrotnie – przekształca mowę na tekst. TTS sprawia, że tekst staje się słyszalny, pomaga osobom z problemami wzroku lub trudnościami w czytaniu. STT zapisuje wypowiedzi jako tekst – przydaje się do dyktowania i sterowania głosem.
Zastosowanie
TTS jest używany w czytnikach e-booków, systemach ogłoszeń i asystentach głosowych, by przekazywać informacje głosowo. STT sprawdza się w transkrypcjach, aplikacjach sterowanych głosem i napisach na żywo dla osób niesłyszących. TTS skupia się na przekazywaniu treści na głos, a STT na przechwytywaniu i przetwarzaniu mowy.
Technologia
TTS analizuje tekst, przetwarza język i syntezuje mowę. Musi oddać intonację i rytm mowy. STT wymaga zaawansowanego rozpoznawania głosu, by dobrze transkrybować różne akcenty, dialekty i sposób mówienia – często w czasie rzeczywistym.
Czym jest TTS (TTS)?
TTS (TTS) to technologia, która zamienia tekst na mowę. W skrócie,TTSpozwala komputerom czytać na głos, zmieniając dowolny tekst w syntetyczny głos. Jest wykorzystywany m.in. w asystentach głosowych i narzędziach dla osób z trudnościami w czytaniu.
Przykładem zaawansowanego TTS jest technologia ElevenLabs. Nasz TTS wyróżnia się naturalnym, ludzkim brzmieniem. Dzięki zaawansowanym algorytmom AI nie tylko naśladuje ludzki głos, ale też rozumie i oddaje niuanse oraz intonację charakterystyczną dla naturalnej mowy.
Tak realistyczny TTS świetnie sprawdza się do tworzenia angażujących treści audio, wzbogacania interfejsów głosowych i jako alternatywa czytania dla osób niewidomych.
Czym jest tekst z mowy (Speech to Text, STT)?
Text from Speech, also known as Speech to Text (STT), is the process of converting spoken language into written text. This speech recognition technology is pivotal in creating transcriptions from audio recordings, enabling voice commands, and facilitating real-time captioning for accessibility.
ElevenLabs made significant advancements in STT technology. Our Scribe model efficiently converting audio and video into text in 99 languages. It offers a user-friendly interface, making it ideal for capturing meetings, lectures, and interviews in written form, from audio and video files.
Jak działa TTS?
TTS zamienia tekst na mowę w kilku krokach.
NajpierwTTS dzieli tekst na fonemy – najmniejsze jednostki dźwięku w języku. To kluczowe, by system poprawnie wymawiał słowa.
Po podziale na fonemy system zamienia je na mowę cyfrową. Tu kluczową rolę odgrywa AI. Dzięki algorytmom uczonym na ogromnych zbiorach nagrań, system generuje mowę zbliżoną do ludzkiej. Gotowa mowa jest dopasowywana do fonemów, co daje naturalny efekt.
Dzięki rozwojowi AI i uczenia maszynowego nowoczesneTTS potrafią rozumieć kontekst, obsługiwać wiele języków i naśladować emocje. To sprawia, że głos brzmi bardziej naturalnie i rozmowy z urządzeniami są przyjemniejsze.
Najlepsi dostawcy TTS
The best TTS software solutions are ElevenLabs, Murf, and PlayHT. Here’s a brief rundown of their main features, pros, cons, and rating out of 5.
Jak działa Speech-to-Text?
Speech-to-Text (STT) zamienia mowę na tekst w kilku krokach.
Najpierw rejestruje wypowiedź, zwykle przez mikrofon. Dźwięk jest zamieniany na format cyfrowy, który system może analizować. Kluczowe jest rozbicie mowy na mniejsze fragmenty przez zaawansowane algorytmy.
Te fragmenty to fonemy, czyli najmniejsze jednostki dźwięku. STT dopasowuje je do wzorców językowych, by rozpoznać słowa i frazy. To ważne przy różnych akcentach i sposobach mówienia.
Następnie system wykorzystuje przetwarzanie języka naturalnego (NLP), by lepiej zrozumieć kontekst i składnię, co zwiększa dokładność transkrypcji. Dzięki temu radzi sobie też z trudniejszymi zdaniami i branżowym słownictwem.
Zaawansowane STT korzystają z uczenia maszynowego i deep learningu, więc im więcej danych, tym lepiej rozpoznają nowe wzorce mowy, akcenty i języki.
Podsumowując, STT to rejestracja dźwięku, analiza fonemów, modelowanie językowe i NLP, a wszystko to wspierane przez AI, by skutecznie zamieniać mowę na tekst.
Najlepsi dostawcy Speech-to-Text
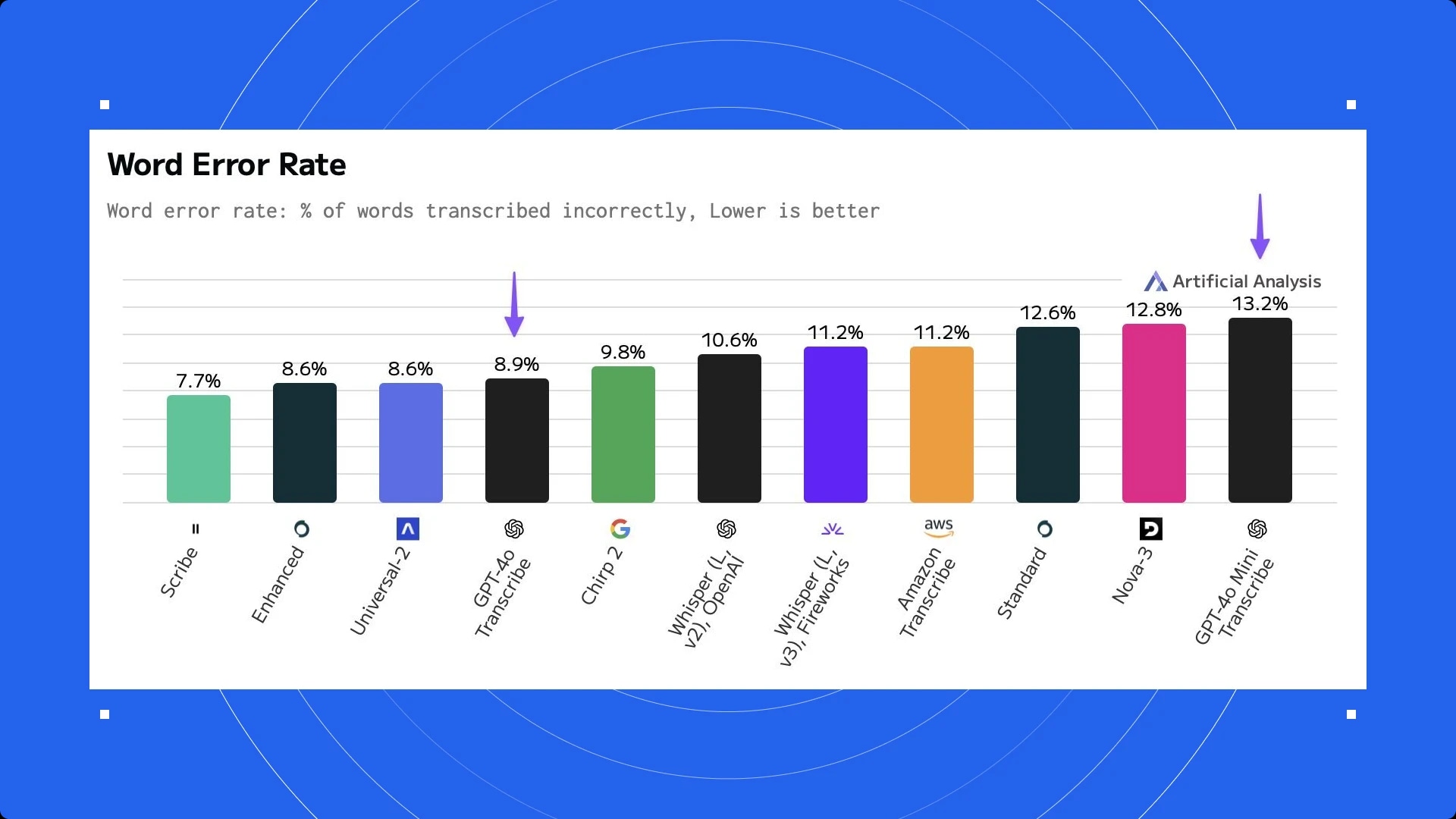
The best speech-to-text providers are ElevenLabs' Scribe, followed by OpenAIand other providers like Google.
TTS i STT: dokładność i wyzwania
TTS i Speech to Text dążą do jak największej precyzji. Ich skuteczność stale rośnie, ale nie są idealne. Oto, czego możesz się spodziewać po obu technologiach.
TTS (TTS): dokładność i wyzwania
Głos AITTS bardzo się rozwinął, ale wciąż są wyzwania. Największym jest osiągnięcie naprawdę naturalnego brzmienia. Nowoczesne TTS potrafią generować wyraźny dźwięk, ale oddanie emocji i intonacji to nadal trudność. TTS czasem źle interpretuje kontekst i przekręca słowa. Kolejnym wyzwaniem jest personalizacja głosów – różne akcenty i style mówienia są kluczowe dla dostępności na całym świecie.
Tekst z mowy/Speech to Text (STT): dokładność i wyzwania
STT jest coraz dokładniejsze, zwłaszcza dzięki deep learningowi. Jednak w hałasie rozpoznawanie głosu bywa trudne. Różnorodność akcentów i dialektów to kolejne wyzwanie. STT ma też problem z homofonami (słowa brzmiące tak samo, ale o innym znaczeniu) i slangiem, co wpływa na skuteczność w praktyce.
Zastosowania w różnych branżach
TTS i Speech to Text mają ciekawe zastosowania w wielu branżach, zmieniając sposób, w jaki korzystamy z informacji i zwiększając dostępność.
Zastosowania TTS w branżach
TTS jest wykorzystywany w edukacji – pomaga tworzyć materiały dostępne dla uczniów z trudnościami w czytaniu lub wzroku, np. zamieniając podręczniki w audiobooki.
W motoryzacji TTS odpowiada za głosowe komunikaty w nawigacji. Obsługa klienta korzysta z TTS do automatycznych odpowiedzi w call center. W branży rozrywkowej, zwłaszcza w grach i asystentach głosowych, TTS zapewnia interaktywne doświadczenia.
Zastosowania STT w branżach
STT ma szerokie zastosowanie. W medycynie pomaga transkrybować rozmowy lekarzy z pacjentami i dyktować dokumentację. W prawie służy do transkrypcji rozpraw i dokumentów. W mediach umożliwia napisy na żywo dla osób niesłyszących. W firmach ułatwia sporządzanie notatek ze spotkań i dostęp do informacji.
Podsumowanie
TTS (TTS) i Speech to Text (STT) to różne technologie. TTS zamienia tekst na mowę, ożywiając treści ludzkim głosem. STT robi odwrotnie – zamienia mowę na tekst, oddając niuanse wypowiedzi.
Obie korzystają z zaawansowanego AI, ale służą innym celom:TTS do słuchania tekstu, a STT do zapisywania mowy.
Chcesz spróbować? Wypróbuj Eleven v3, nasz najbardziej ekspresyjny model text-to-speech.
Jeśli chcesz poznać najnowszą technologię TTS,zarejestruj się w ElevenLabs już dziś. Nie pożałujesz.

Przeglądaj artykuły zespołu ElevenLabs

Tutore deploys conversational agents for corporate language training using ElevenLabs
90% of Tutore’s placement interviews are now conducted by AI agents, accelerating onboarding and reducing costs
.webp&w=3840&q=95)
Introducing Music Finetunes in ElevenCreative
Generate individual vocals, instruments or full tracks with stylistic consistency using a fine-tuned version of our Music model.

